Content syndication is a powerful lead generation tool. It’s a great way to get your content in front of a large audience in a short time compared to simply posting it on your website.
It also means republishing your content on multiple sites simultaneously—simply duplicating the material. Essentially it allows you to increase the content’s reach and attract new audiences.
It’s a proven way to generate high quality leads for your sales team without spending too much money on creating new content.
At this point, you might be wondering what the best way to do this is. Keep reading—this blog will cover the best content syndication practices you need to know to make the most of it.
Let’s start with the basics.
What is Content Syndication?
Content syndication refers to sharing the same piece of content—whether it’s a blog article, infographic, or video—across different websites.
Platforms of all sizes syndicate such content because it helps them bring traffic to their websites with fresh information. It’s a kind of barter system: your brand reaches a new audience, and the platform benefits from increased traffic.
How Does Content Syndication Work?
Content syndication is a straightforward process that involves four primary steps:
1. Create High-Quality Content:
To succeed with content syndication, start with valuable, relevant content, such as blog posts, articles, whitepapers, e-books, videos, or infographics.
2. Identify the Right Syndication Partners:
Select third-party platforms, such as industry publications or media sites, that cater to your target audience. The right partners are those whose audience aligns well with your brand and who can deliver your message effectively.
3. Publish and Distribute:
Partner with your syndication partners. Some platforms allow for full syndication (republishing the entire piece), while others prefer partial syndication. Choose the option that suits you best.
4. Measure and Optimize:
Use analytics to track metrics like engagement, referral traffic, lead conversions, and overall performance. Based on these insights, refine your approach to improve future syndication efforts.
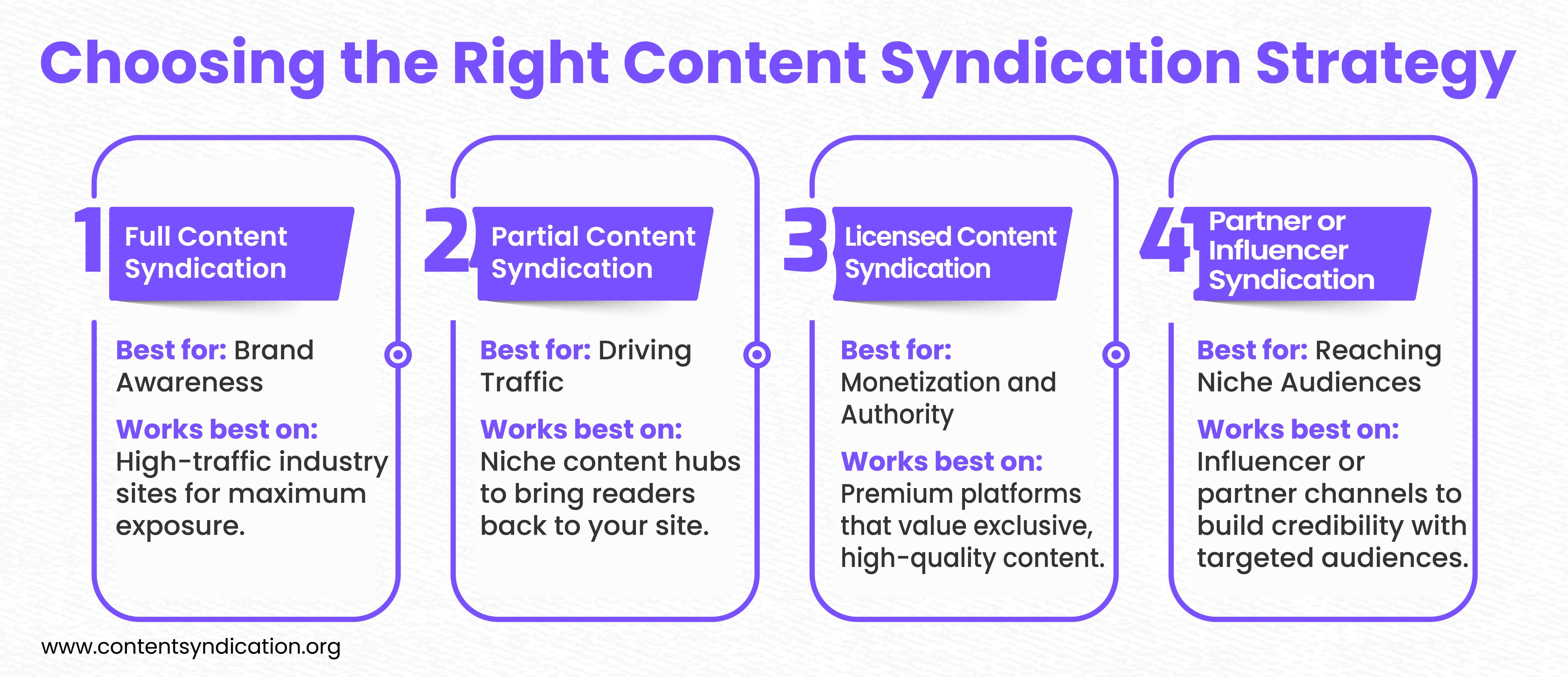
Types of B2B Content Syndication
Content syndication isn’t one-size-fits-all. Here are the primary types, each with unique benefits and challenges.
1. Full Content Syndication
With full content syndication, your entire piece is republished on a third-party site. While this maximizes exposure, it requires careful handling of SEO to avoid duplicate content penalties.
- Benefits:
- Maximizes reach by presenting the full content to a wider audience.
- Great for building brand visibility on trusted platforms.
- Challenges:
- Risks duplicate content penalties if not handled correctly.
- Requires canonical tags to direct search engines to the original source, preserving SEO integrity.
2. Partial Content Syndication
Partial syndication involves publishing an excerpt, summary, or snippet of your content with a link back to the full piece on your website. This helps retain SEO benefits and drives traffic back to your site.
- Benefits:
- Drives traffic directly to your site, boosting engagement.
- Helps preserve SEO by linking back to the original content.
- Challenges:
- May limit content exposure compared to full syndication.
- Requires compelling excerpts to entice readers to visit your site.
3. Licensed Content Syndication
In licensed syndication, content is licensed to third-party platforms in exchange for a fee or other form of monetization. This approach works best for high-value content like research reports, whitepapers, or videos.
- Benefits:
- Monetizes your content while expanding reach.
- Often features high-quality, gated content that positions your brand as an authority.
- Challenges:
- Requires consistent, high-quality, exclusive content to maintain value.
- Licensing terms and partnerships need to be carefully managed.
4. Partner or Influencer Syndication
In this type of syndication, brands collaborate with influencers, industry leaders, or business partners to distribute content across their channels. This allows brands to reach a highly relevant, engaged audience through trusted voices.
- Benefits:
- Reaches a targeted audience through established, credible figures in the industry.
- Builds credibility and brand authority through endorsement by trusted influencers or partners.
- Challenges:
- Requires strong relationships and alignment with influencers or partners to ensure brand consistency.
- Results may vary depending on influencer reach and audience engagement.
Must Read: Paid Content Syndication: Reach More Leads in Less Time
Key Benefits of B2B Content Syndication
Content syndication is valuable for introducing your brand to new audiences and building long-term customer relationships. Content syndication, in particular, can generate more leads by delivering the right message to your audience.
Here are some Benefits of B2B Content Syndication
- Enables you to create and publish content across multiple websites.
- Provides access to high-authority sites, increasing brand credibility.
- Improves search engine rankings
- Increases traffic by adding backlinks to your website.
- Generates high-quality leads from relevant audiences.
- Re-engages old leads who may have lost interest or drifted away.
- Maximizes return on investment (ROI) by creating content once and distributing it widely.
Imagine this: Your latest industry report, previously limited to your website visitors, is now featured on high-traffic sites and popular industry blogs. Suddenly, potential customers from previously untapped corners of the web are discovering your brand. Such leads are more engaged and interested, meaning your sales team can focus on more promising prospects rather than cold leads.
And identifying leads early in the customer journey, you can concentrate on those most likely to convert into paying customers.
Must Read: Choosing the Right Content Syndication Network.
Best Practices for Content Syndication Success
To make the most of content syndication, follow these best practices:
1. Create Evergreen Content
Content syndication works only for trending content, right? Well, that’s a myth. It’s particularly effective for evergreen content—such as guides, how-to's, and industry insights—because it retains its relevance over time, continuously attracting readers long after its initial publication.
2. Choose Reputable Syndication Partners
With so many high-impact platforms available, choosing the right one is difficult. So, how do you choose the best one?
Start with a shortlist of reputable, industry-specific platforms and review engagement metrics like social shares or audience demographics.
Next, evaluate each partner's performance over time and refine your partnerships based on results.
3. Use Canonical Tags for SEO
Content syndication means duplication? Right.
It harms SEO? Wrong.
What’s correct way? Use canonical tags on syndicated content. This signals to search engines that your website is the primary source, avoiding SEO penalties and preserving your rankings.
Make sure you communicate SEO guidelines clearly when setting up syndication agreements and follow up with partners to verify compliance. Lastly, regularly audit syndicated content to confirm that SEO practices are in place.
4. Experiment with Different Syndication Types
Is only one type of syndication effective for all audiences and goals?
No because different syndication types (full, partial, influencer) offer distinct benefits. So, aim for a balanced mix to maximize reach and engagement.
5. Track and Optimize Performance
Once syndicated, there’s no need for further monitoring. It’s a myth. In reality, you need to regularly track metrics like referral traffic, lead conversions, and page views.
You can also use UTM parameters and analytics tools to track metrics. It’s important to capture data from all syndication sources.
Additionally, establish a regular review process to analyze this data and adjust your strategy as needed.
In Conclusion
Content syndication is a wonderful opportunity to reach new audiences and convert them into leads.
A well-planned and a well-executed b2b content syndication campaign can give a huge boost to your ROI.
When done right, content syndication can help you reach new audiences, establish your brand as a thought leader, and ultimately grow your revenue.
Must Read: AI and Intent Data are Transforming B2B Content Syndication
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is content syndication?
Content syndication is the process of republishing your original content (such as blogs, whitepapers, case studies, or eBooks) on third-party websites to expand its reach, attract new audiences, and generate leads.
How does B2B content syndication work?
In B2B content syndication, companies share valuable content across partner networks or publishing platforms where their target audience is already active. This content is used to attract high-quality leads, often collected through gated forms or targeted email campaigns.
What types of content are best for syndication?
Content that performs well in syndication includes:
- Whitepapers
- eBooks
- Case studies
- Webinars
- Industry reports
- Blog posts
- Infographics
Is content syndication good for SEO?
Content syndication can be SEO-friendly if done correctly. Use canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues and ensure that backlinks point to your original piece to improve authority.
What are the benefits of content syndication?
Key benefits include:
- Increased brand awareness
- Expanded audience reach
- Higher content ROI
- Enhanced lead generation
- Improved content lifespan
How is content syndication different from guest posting?
Guest posting involves writing new content for another site, whereas syndication repurposes existing content on new platforms. Both aim to boost visibility, but syndication is more scalable for promoting high-performing assets.
Can I control where my content is syndicated?
Yes. With strategic syndication partners or platforms, you can define industry, geography, job titles, and company size to ensure your content reaches the most relevant audience.
Is content syndication pay-to-play?
It depends. There are free syndication methods like Medium and LinkedIn, and paid syndication options where content is distributed via premium platforms with guaranteed lead generation.
How do I measure the success of content syndication?
Track metrics such as:
- Lead quality and volume
- Engagement rate (clicks, downloads)
- Conversion rate
- Cost per lead (CPL)
- Return on investment (ROI)
Does Only B2B offer content syndication services?
Yes. Only B2B specializes in multi-channel content syndication tailored for B2B tech companies, using intent data and precise targeting to generate qualified leads.




